Minority Rights
Helsinki Commission Deeply Concerned Over Latest Ele...
Jul 27, 2022WASHINGTON—Helsinki Commission Chairman Sen. Ben Cardin (MD) and Co-Chairman Rep. Steve Cohen (TN-09) today expressed deep concern about an effort by the international community’s High Representative in Bosnia to impose […]
30 Years After Ovcara
Nov 19, 2021By Robert Hand, Senior Policy Advisor On November 20, 1991, after the fall of the city of Vukovar in Croatia, militant Serb forces removed 265 ill and injured Croats from […]
Cardin and Wicker Discuss July 2021 Congressional De...
Jul 21, 2021Mr. CARDIN. Madam President, I take this time to talk about the work of the U.S. Helsinki Commission in a recent opportunity we had to participate in the OSCE Parliamentary […]
Helsinki Commission Delegation Advances Priority Iss...
Jul 15, 2021WASHINGTON—Helsinki Commission Chairman Sen. Ben Cardin (MD) and Ranking Member Sen. Roger Wicker (MS) last week led a U.S. delegation to the 2021 OSCE Parliamentary Assembly (PA) Annual Session in […]

Helsinki Commission Commemorates 45 Years of Advanci...
Jun 03, 2021WASHINGTON—To commemorate the 45th anniversary of the Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, also known as the U.S. Helsinki Commission, on June 3, Chairman Sen. Ben Cardin (MD) and […]
Helsinki Commission Leaders Commemorate Internationa...
Apr 08, 2021WASHINGTON—Ahead of International Roma Day on April 8, Helsinki Commission Chairman Sen. Ben Cardin (MD), commission leaders the late Rep. Alcee L. Hastings (FL-20) and Sen. Roger Wicker (MS), and […]
U.S. Election Practices: An International Perspective
Mar 16, 2021Madam Speaker, this chamber recently passed H.R. I, the “For the People Act,” significant legislation making it easier for American citizens to vote in U.S. elections and improve transparency and […]
Chairman Hastings Introduces Federal Jobs Act to Inc...
Feb 19, 2021WASHINGTON—Helsinki Commission Chairman Rep. Alcee L. Hastings (FL-20) on Thursday reintroduced the Federal Jobs Act, a bill to establish a government-wide diversity and inclusion plan to ensure fair access and […]
Chairman Hastings Introduces LITE Act to Foster Shar...
Feb 18, 2021WASHINGTON—Helsinki Commission Chairman Rep. Alcee L. Hastings (FL-20) on Thursday reintroduced the Leadership Institute for Transatlantic Engagement (LITE) Act to strengthen ties with U.S. allies, protect democratic institutions, and support […]
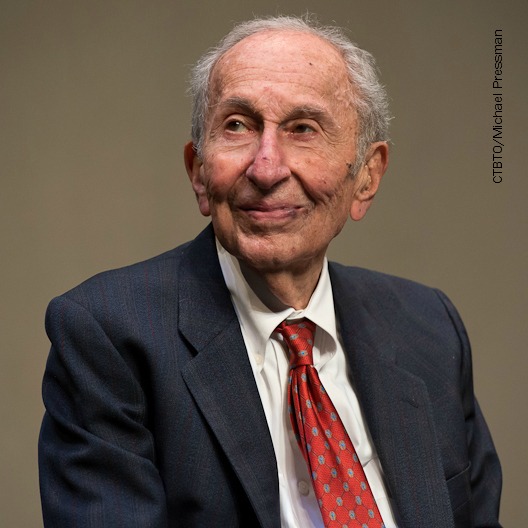

Ambassador Max Kampelman’s Contributions to the Hels...
Jan 25, 2021By Emma Derr, Max Kampelman Fellow The Helsinki Commission’s flagship fellowship program recognizes former U.S. Ambassador Max Kampelman, who spent his life working toward comprehensive security at home and across […]
Retrospective on the 116th Congress
Dec 18, 2020By Emma Derr, Max Kampelman Fellow “For more than four decades, the Helsinki Commission has championed human rights and democracy across North America, Europe, and Central Asia. While we have […]
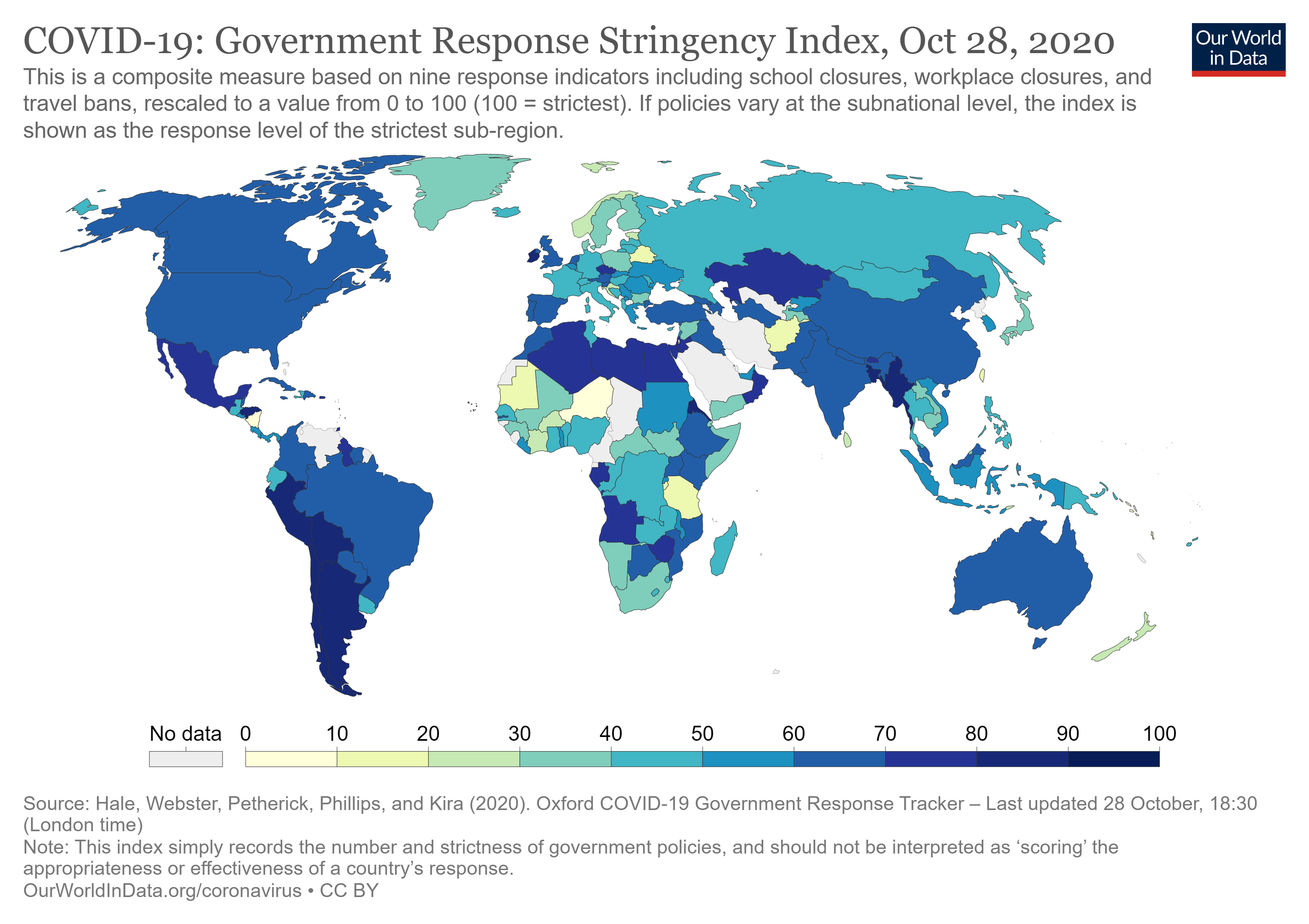
Coronavirus in the OSCE Region
Oct 30, 2020By Emma Derr, Max Kampelman Fellow A novel coronavirus was first identified in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Termed COVID-19, the disease spread rapidly around the globe. As of October […]
