Freedom of Movement
Saving Ukraine’s Children
Dec 14, 2022Ukraine’s children are suffering serious injury and trauma due to Russia’s genocidal war on Ukraine. Almost two-thirds of the country’s children have been displaced. Thousands have been injured and, although […]
Helsinki Commission Delegation Advances Priority Iss...
Jul 15, 2021WASHINGTON—Helsinki Commission Chairman Sen. Ben Cardin (MD) and Ranking Member Sen. Roger Wicker (MS) last week led a U.S. delegation to the 2021 OSCE Parliamentary Assembly (PA) Annual Session in […]

Helsinki Commission Commemorates 45 Years of Advanci...
Jun 03, 2021WASHINGTON—To commemorate the 45th anniversary of the Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, also known as the U.S. Helsinki Commission, on June 3, Chairman Sen. Ben Cardin (MD) and […]
Helsinki Commission Condemns Lukashenko Regime for F...
May 24, 2021WASHINGTON—Following Alexander Lukashenko’s order to divert and forcibly land a commercial plane in Minsk in order to arrest Belarusian activist and journalist Raman Pratasevich and civil society activist Sofia Sapega, […]
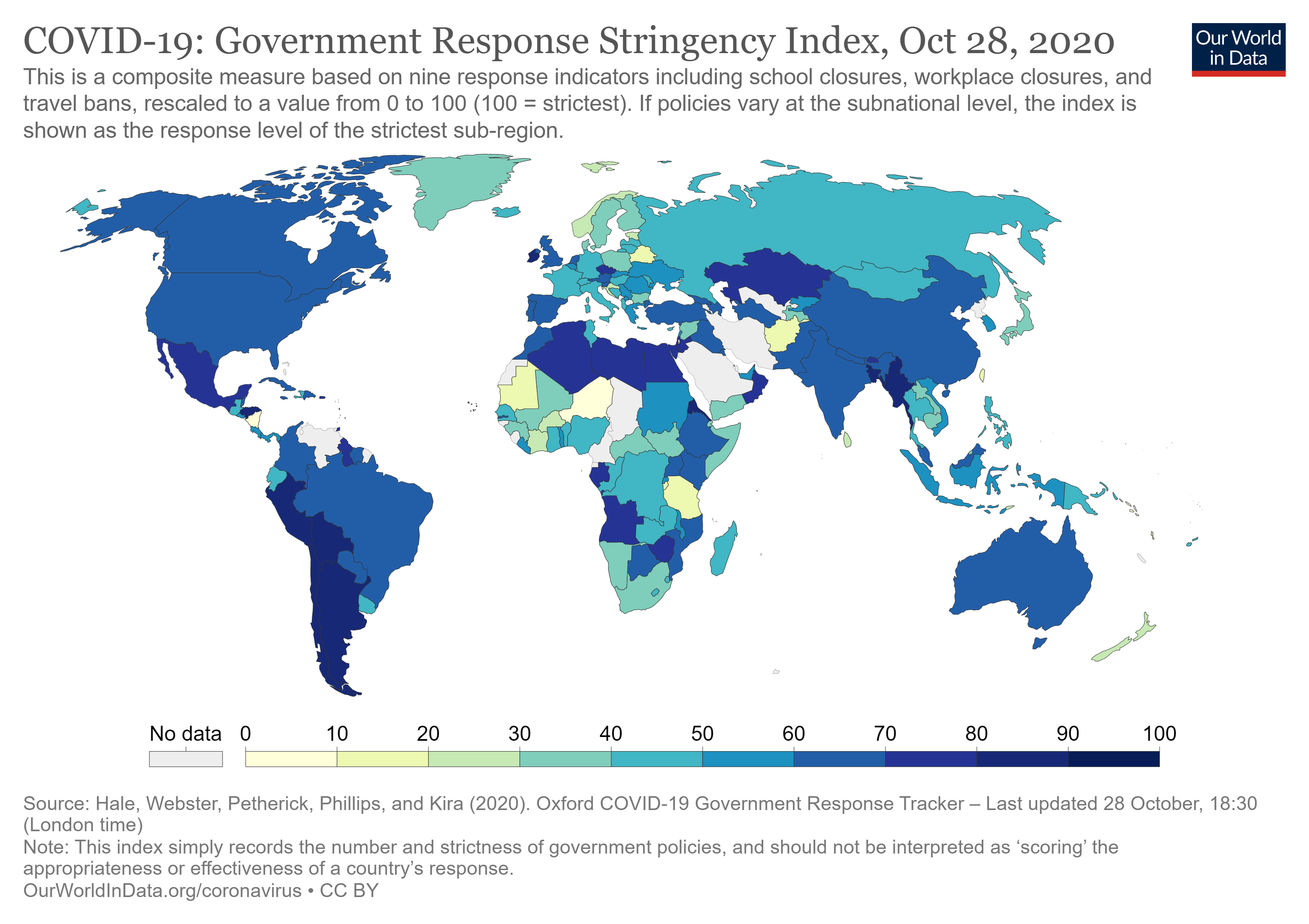
Coronavirus in the OSCE Region
Oct 30, 2020By Emma Derr, Max Kampelman Fellow A novel coronavirus was first identified in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Termed COVID-19, the disease spread rapidly around the globe. As of October […]

ONGOING TRANSATLANTIC ENGAGEMENT THROUGH THE OSCE PA...
Sep 24, 2020Mr. HUDSON. Madam Speaker, I rise today to highlight my recent efforts to engage with our allies across Europe to address the current political turmoil in Belarus and seek a […]

Hastings: Petty Parochialism Denies OSCE Vital Leade...
Jul 14, 2020WASHINGTON—Following yesterday’s failure of OSCE representatives to renew the mandates of four leadership positions—the OSCE Secretary General, the High Commissioner on National Minorities, the Representative on Freedom of the Media, […]
Wicker and Cardin Commend United Kingdom Magnitsky S...
Jul 07, 2020WASHINGTON—Following the recent designations under the United Kingdom’s Magnitsky sanctions framework of Russian and Saudi officials responsible for the deaths of Sergei Magnitsky and Jamal Khashoggi, Helsinki Commission Co-Chairman Sen. […]
Human Rights and Democracy in a Time of Pandemic
May 12, 2020The outbreak of the novel coronavirus pandemic has prompted governments around the world to take extraordinary measures in the interest of public health and safety. As of early April, nearly […]
Wicker and Cardin Urge Pompeo to Work with EU High R...
May 11, 2020WASHINGTON—In a letter released today, Helsinki Commission Co-Chairman Sen. Roger Wicker (MS) and Ranking Member Sen. Ben Cardin (MD) urged U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo to ask the EU’s […]
Reflecting on Chechnya
Mar 13, 2020By Mia Speier, Max Kampelman Fellow On December 11, 1994, Russian forces advanced into Chechnya, a republic in the North Caucasus near Georgia and Azerbaijan, to stop an attempt at […]
Human Rights and Democracy
Jan 29, 2020For nearly three decades, the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights (ODIHR) has been at the forefront of efforts to promote […]
