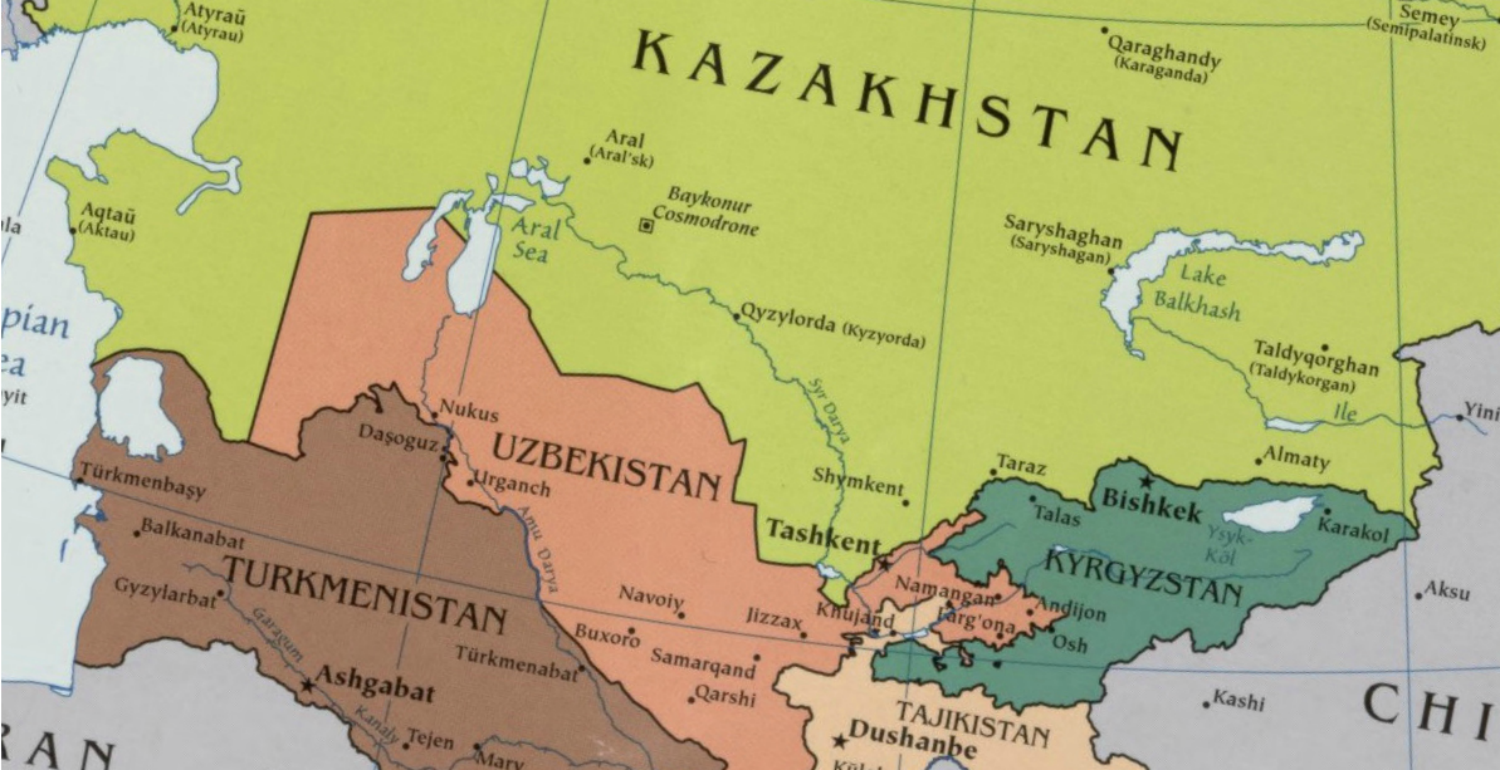
This briefing proposed the question of what the impact will be in the Central Asian region as the United States prepares to leave Afghanistan. This strategy will particularly impact the economies of Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan, as the United States has accelerated efforts to integrate Afghanistan with the economies of these countries.
Witnesses testifying at this briefing addressed the ability of these governments to create the necessary conditions for more trade and exchange, including infrastructure development, efficient customs regimes and reliable transportation networks. The deep political divisions in this region that prevent collaboration on basic necessities such as water and electricity were also identified as hindrances to building greater economic cooperation. These issues were analyzed in the context of the current situation and the future outlook for economic development along the New Silk Road.