Tajikistan
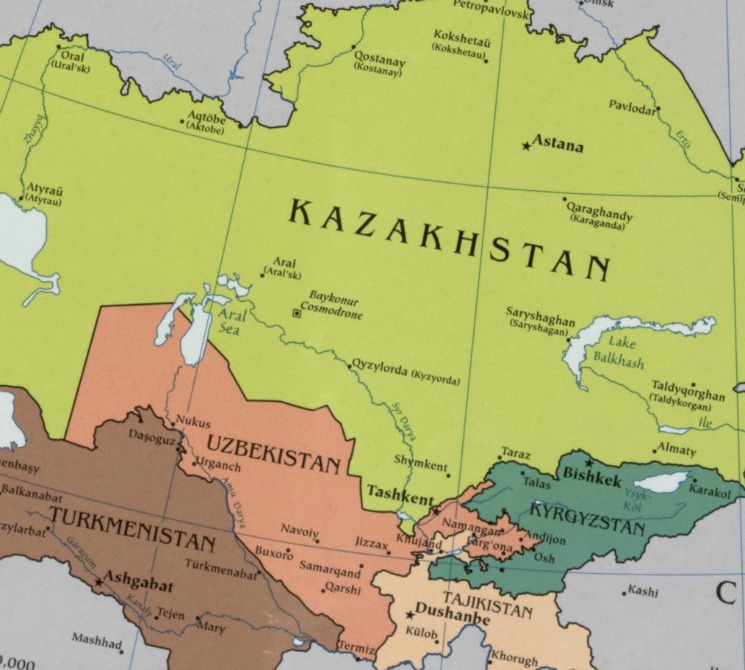
BRIEFING—The Impact on Central Asia of Russia’s War ...
Sep 04, 2025Rayburn House Office Building 2200 Stream live here Russia’s war on Ukraine has had a significant impact on the countries of Central Asia, including shifting their relationships with Russia and […]

The Impact on Central Asia of Russia’s War on Ukrain...
Sep 04, 2025Russia’s war on Ukraine has had a significant impact on the countries of Central Asia, including shifting their relationships with Russia and China and reshaping their internal political and economic […]

Helsinki Commission Advances Human Rights, Demands f...
Oct 19, 2023By Shannon Simrell, Senior Policy Advisor Between October 2-13, 11 Helsinki Commission staff joined approximately 1,400 representatives of OSCE participating States (pS) and civil society representatives in Warsaw, Poland in […]
Co-Chairman Cohen, Ranking Member Wilson Introduce T...
Jul 30, 2021WASHINGTON—Helsinki Commission Co-Chairman Rep. Steve Cohen (TN-09) and Ranking Member Rep. Joe Wilson (SC-02) yesterday introduced the Transnational Repression Accountability and Prevention (TRAP) Act in the U.S. House of Representatives. […]
Sweden’s Leadership of the OSCE
Jun 11, 2021In 2021, Sweden chairs the world’s largest regional security organization—the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)—which comprises 57 participating States stretching from North America, across Europe, and to […]
Swedish Foreign Minister Ann Linde to Appear at Hels...
Jun 03, 2021WASHINGTON—The Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, also known as the Helsinki Commission, today announced the following online hearing: SWEDEN’S LEADERSHIP OF THE OSCE Priorities for 2021 Friday, June […]

Helsinki Commission Commemorates 45 Years of Advanci...
Jun 03, 2021WASHINGTON—To commemorate the 45th anniversary of the Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, also known as the U.S. Helsinki Commission, on June 3, Chairman Sen. Ben Cardin (MD) and […]
Helsinki Commission Leaders Mark World Press Freedom...
May 03, 2021WASHINGTON—On World Press Freedom Day, Helsinki Commission Chairman Sen. Ben Cardin (MD) and commission leaders Sen. Roger Wicker (MS) and Rep. Joe Wilson (SC-02) issued the following statements: “Press freedom […]
OSCE Ministerial Council Appoints Top Leaders, Adopt...
Dec 21, 2020By Shannon Simrell, Representative of the Helsinki Commission to the U.S. Mission to the OSCE Foreign ministers of the 57 OSCE participating States convened on December 3 – 4, 2020, […]

Helsinki Commission Digital Digest: December 2020
Dec 21, 2020Co-Chairman Wicker on Secretary of State’s New Desig...
Dec 10, 2020WASHINGTON—Following U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo’s December 7 designations for Countries of Particular Concern (CPC) and the Special Watch List for the worst religious freedom violations, Helsinki Commission Co-Chairman […]

Albanian Prime Minister Edi Rama to Appear at Helsin...
Sep 09, 2020WASHINGTON—The Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, also known as the Helsinki Commission, today announced the following online hearing: ALBANIA’S CHAIRMANSHIP OF THE OSCE Responding to the Multiple Challenges […]
